Unit 3 – Periodic Table and Periodicity of Properties (Short Questions)
Q.1 Why noble gases are not reactive?
Q.2 Why Cesium (at.no.55) requires little energy to release its one electron present in the outermost shell?
Q.3 How is periodicity of properties dependent upon number of protons in an atom?
Q.4 Why shielding effect of electrons makes cation formation easy?
Q.5 What is the difference between Mendeleev’s periodic law and modem periodic law?
Q.6 What do you mean by groups and periods in a Periodic Table?
Q.7 Why and how are elements arranged in 4th period?
Q.8 Why the size of atom does not decrease regularly in a period?
Q.9 Give the trend of ionization energy in a period.
Q.1 Why noble gases are not reactive?
Answer:
Noble gases are not reactive because they have their valence shells completely filled.
They have 2 or 8 electrons in their valence shells. Their atoms do not have vacant spaces in their valence shell to accommodate more electrons. Therefore they do not gain, lose or share electrons.
Q.2 Why Cesium (at.no.55) requires little energy to release its one electron present in the outermost shell?
Answer:
Cesium requires little energy because it has greater atomic size, more shielding effect (due to presence of more electrons) and low ionization energy due to which the hold of inner nucleus on valence.
Q.3 How is periodicity of properties dependent upon number of protons in an atom?
Answer:
Number of protons in an atom represents atomic number of that element which increases regularly by one form element to element. So the arrangement of elements according to increasing atomic number shows the periodically in the electronic configuration of the elements that leads to periodicity in their properties.
Q.4 Why shielding effect of electrons makes cation formation easy?
Answer:
The shielding effect of electrons makes the cation formation easy because it reduces the nuclear pull on the outermost electrons and they are less tightly held by the nucleus and can easily be lost from the outermost shell.
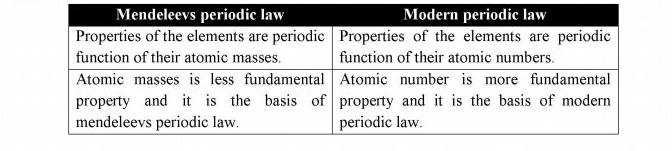
Q.5 What is the difference between Mendeleev’s periodic law and modem periodic law?
Answer:
Q.6 What do you mean by groups and periods in a Periodic Table?
Answer:
The horizontal rows of elements in a periodic table are called periods. The vertical columns in a periods table are called group. There are 18 groups in the long form of the periodic table. They are studied from top to bottom.
Q.7 Why and how are elements arranged in 4th period?
Answer:
The elements (Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl and Ar) are arranged in the 4th period because they are all having four electronic shells and are arranged by increasing atomic number from left to right the period.
Q.8 Why the size of atom does not decrease regularly in a period?
Answer:
The size of atom does not decrease regularly in a period. This irregularity in the transition metals is due to the involvement of d orbital. It provides poor shielding effect.
Q.9 Give the trend of ionization energy in a period.
Answer:
ionization energy increases from left to right in a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group.
Reason:
It is because the size of atoms reduces and valence electrons are held strongly by the electrostatic force of nucleus.