Unit 10 – Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves(Short Questions)
Q.1 What is meant by oscillation?
Q.2 Define Simple Harmonic Motion.
Q.3 Define Hooke’s Law. Give its expression.
Q.4 How does stiffness of the spring affect the value of k?
Q.5 What is the function of restoring force during oscillatory motion?
Q.8 Define following terms which characterize simple harmonic motion.
Q.9 Write down important features of Simple Harmonic Motion.
Q.10 Define time period and frequency in case of vibratory motion.
Q.11 Differentiate between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
Q.12 Differentiate between transverse waves and compressional or longitudinal waves.
Q.13 Write down the relationship between frequency and time period.
Q.14 If we double the length of the pendulum then what will be the time period?
Q.16 What is meant by damped oscillation?
Q. 17 How does the mechanical energy of system reduce?
Q. 18 How a wave can be defined? In which categories are these divided?
Q. 19 Define electromagnetic waves and give its examples.
Q.20 Define mechanical waves. Give examples.
Q.21 Do the mechanical waves pass through a space?
Q.22 Define longitudinal or compressional waves?
Q. 23 Differentiate between crest and trough?
Q.26 A wave moves on a slinky with frequency of
4 Hz and wavelength of 0.4 m. What is the speed of the wave?
Q. 27 Why bright lines are seen on the screen of the ripple tank?
Q.28 Why dark lines are seen on the screen of the ripple tank?
Q.29 How can we generate circular waves in a ripple tank?
Q. 30 Why does wavelength decrease in shallow part of water?
Q. 31 How diffraction is useful in daily life?
Q. 32 How do ocean waves cause destruction?
From Board Papers
Q.1 What is spring constant? Write its formula.
Q.2 Define waves equation and write its formula.
Q. 3 What is meant by wavelength?
Q.4 What is the function of Ripple Tank?
Q. 5 Define refraction of waves.
Q.8 Define SHM. Also write features of SHM.
Q.9 . Define simple pendulum. Write down its time period equation/formula.
Q.10 What is meant by vibration?
Q.11 Define damped oscillations. Give its two examples for daily life.
Q.12 Define wave motion.
Q.13 Define longitudinal waves.
Q. 15 Define electromagnetic waves. Also give an example.
Q.17 Define wave.
Q.19 What is meant by compression?
Q.20 Define mechanical waves and give example.
Q.21 What is difference between Mechanical Waves and Electromagnetic Waves?
Q.22 What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves?
Q.23 Define diffraction of waves.
Q.24 Define reflection of waves.
Q.25 State Hook’s law.
Q.26 Define a time period. Write the formula of time period of a simple pendulum.
Q.27 Define frequency and write its unit.
1. What is meant by oscillation?
Answer: When a body moves back and forth or to and fro about its mean position. is called vibration or oscillation.
Example: Motion of the Simple Pendulum.
2. Define Simple Harmonic Motion.
Answer: The acceleration of a body executing SHM is directly proportional to the displacement of the body from the mean position and is always directed towards the mean position ∝
Mathematically : a ∝ – x
Where a is acceleration. It is always directed towards the mean position and x is displacement from mean position.
3. Define Hooke’s Law. Give its expression.
Answer: According to Hooke‘s law the exerted force is directly proportional to change in length.
4. How does stiffness of the spring affect the value of k?
Answer: The value of k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. Stiff springs have large k values, and soft springs have small k values.
5. What is the function of restoring force during oscillatory motion?
Answer: A restoring force always pushes or pulls the object performing oscillatory motion towards the mean position.
6. Which type of forces are acting on a displaced pendulum? OR Which component of force act as restoring force during the oscillation of simple?
Answer: The restoring force that causes the pendulum to undergo simple harmonic motion is the component of gravitational force mg sinθ tangent to the path of motion.
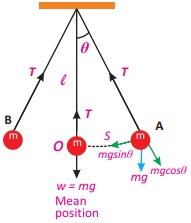
7. Define Time Period and Write down formulas of Time Period for mass attached to a spring and for simple Pendulum?
Answer:
Time Period (T):
Time required to complete one vibration is called time period. It is denoted by T.
The time period T of the simple harmonic motion of a mass m attached to a spring is given by the following equation:
Formula for the time period of simple pendulum:
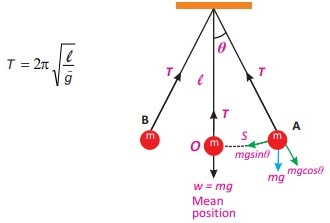
8. Define following terms which characterize simple harmonic motion.
(i) Vibration (ii) Time period (iii) Frequency (iv) Amplitude (v) Displacement
Answer: (i) Vibration: One complete round trip of a vibrating body about its mean position is called one vibration.
(ii) Time period: The time taken by a vibrating body to complete one vibration is called time period.
(iii) Frequency: The number of vibrations per cycle of a vibrating body in one second is called its frequency. It is reciprocal of time period i.e f= 1/T
(iv) Amplitude: The displacement of a vibrating body on either side from its mean position to extreme position is called its amplitude.
(v) Displacement: Distance covered by the vibrating body at any instant during the vibration from mean position.
Q.9 Write down important features of Simple Harmonic Motion.
Important features of SHM are summarized as:
- A body executing. SHM always vibrates about a fixed position.
- Its acceleration is always directed towards the mean position
- The magnitude of acceleration is always directly proportional to its displacement from the mean position i.e. acceleration will be zero at the mean position while it will be maximum at the extreme positions.
- Its velocity is maximum at the mean position and zero on the extreme positions.
Q.10 Define time period and frequency in case of vibratory motion.
Answer:
Time Period
vibratory motion:
The time required to complete one vibration is known as time period.
Waves:
The time required to pass one wave from a certain point is called time period.
T = 1/f
Frequency:
vibratory motion:
The number of vibrations completed in one second is known as frequency
Waves:
The number of waves passing through a certain point in one second is known as frequency.
Q.11 Differentiate between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
Answer:
Mechanical Waves:
The waves which require a material medium for their propagation are known as mechanical waves.
Examples:
i. Sound waves
ii. Waves produced on a rope
iii. Water waves
Electromagnetic Waves:
The waves which can propagate with or without material medium are known electromagnetic waves.
Examples:
i. X–rays
ii. Radio waves
Q.12 Differentiate between transverse waves and compressional or longitudinal waves.
Transverse Waves:
The waves in which the direction of vibratory motion of particles of medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves are called transverse waves.
Examples:
i. Waves produced in a rope
ii. Water waves
Compressional or Longitudinal Waves:
The waves in which the direction of vibratory motion of particles of medium is parallel to the direction of propagation of waves are called compressional or longitudinal waves.
Q.13 Write down the relationship between frequency and time period.
Answer: Frequency is a reciprocal of time period (They have inverse relationship).
Q.14 If we double the length of the pendulum then what will be the time period?
Answer: As we know that
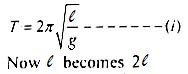
So
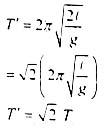
Hence Time Period is √2 times of time period.
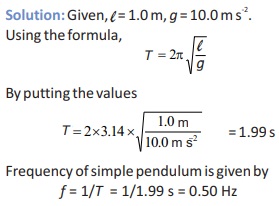
Q.15 Find the time period and frequency of a simple pendulum 1.0 m long at a location where g = 10.0 m s-2 .
Answer:
Q.16 What is meant by damped oscillation?
Answer: The oscillations of a system in the presence of some resistive force are damped Oscillations.
Q. 17 How does the mechanical energy of system reduce?
Answer: The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped, this damping progressively reduces the amplitude of the motion.
Q. 18 How a wave can be defined? In which categories are these divided?
Answer:
A wave is a disturbance in the medium which causes the particles of the medium to undergo vibratory motion about their mean position in equal intervals of time.
There are two categories of waves. (i) Mechanical waves (ii) Electromagnetic Waves
Q. 19 Define electromagnetic waves and give its examples.
Answer: Waves which do not require any medium for their propagation are give called electromagnetic waves
Examples:
Q.20 Define mechanical waves. Give examples.
Answer:
Waves which require any medium for their propagation are called mechanical waves.
Examples:
1. Water waves
Q.21 Do the mechanical waves pass through a space?
Answer:
No, mechanical waves do not pass through the space because they require medium for their propagation.
Q.22 Define longitudinal or compressional waves?
Answer:
The waves in which the particles of medium move back and forth along the direction of the propagation of wave are called longitudinal or compressional waves.
Q. 23 Differentiate between crest and trough?
Answer:
Crest: The highest point on the wave is called crest.
Trough: The lowest point on the wave is called trough.
Q.24 Define transverse waves?
The wave in which the particle of medium moves perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave.
Example:
Q.25 What is wave equation?
Answer:
The relation between the velocity, frequency and wavelength of the wave is known as wave equation.
Q.26 A wave moves on a slinky with frequency of
4 Hz and wavelength of 0.4 m. What is the speed of the wave?
Solution: Given that, f = 4 Hz, λ = 0.4 m
Wave speed v = fλ
v = (4 Hz) (0.4 m)
v = 1.6 m s-1
Q. 27 Why bright lines are seen on the screen of the ripple tank?
Answer: The crests of the waves appear as bright lines on the paper because they behave like a convex lens and converge the rays of light falling on them. So, bright lines are seen on the screen of the ripple tank.
Q.28 Why dark lines are seen on the screen of the ripple tank?
Answer: The troughs of the waves appear as dark lines on the paper because they behave like a concave lens and diverge the rays of light falling on them. So, dark lines are seen on the screen of ripple tank.
Q.29 How can we generate circular waves in a ripple tank?
Answer: We can generate circular waves in a ripple tank by attaching a knob on the lower side of vibrating bar. Now it is lowered in such a way that knob touches the water surface. When vibrator is set on, circular waves are produced on the water surface.
Q. 30 Why does wavelength decrease in shallow part of water?
Answer: As wavelength changes with the depth of water so there will be a decrease in wavelength of the waves in shallow part of water due to decrease in the speed of the waves.
Q. 31 How diffraction is useful in daily life?
Answer: Due to diffraction of radio waves, transmission can be heard in such areas where the waves cannot reach directly.
Q. 32 How do ocean waves cause destruction?
Answer: Sometime, the ocean waves cause the destruction of ships and coastal areas because in case of any disturbance in the ocean, energy is carried by the waves and they travel towards coastal area and causes destruction.
Q.1 What is spring constant? Write its formula?
Answer: Definition: The ratio of force (F) acting on the spring to the displacement (x ) from mean position.
Formula: According to Hook’s law, F =-kx
Where k is spring constant. It is defined as k = F/x
Value of k is measurement of stiffness of the spring. It Sl unit is Nm-1
Q.2 Define waves equation and write its formula.
Answer: Waves equation: An equation which provides us relation between wavelength (λ) frequency (f) and velocity of waves (v) is called wave
equation.
Q. 3 What is meant by wavelength?
Answer: Wavelength: Wavelength means length of wave.
Definition: Wavelength is the distance between two identical adjacent crest or trough.
Symbol: Wavelength represented by λ.
Unit: The unit of wavelength is metre (m).
Q.4 What is the function of Ripple Tank?
Answer: Ripple Tank: Ripple tank is a device used to produce water waves to study their characteristics (reflection, refraction, (diffraction)
Q. 5 Define refraction of waves.
Answer: Refraction of waves: When a wave from one medium enters into the second medium at some angle, its direction of travel changes. It is called refraction of waves.
Q. 6 Define Restoring Force.
Answer: Definition: A restoring force always pushes or pulls the object performing oscillatory motion towards the mean position.
Unit: The unit of restoring force is Newton (N).
Example: Suppose that mass ‘m’ is pulled through a distance ‘x’ up to extreme position ‘A’ and then released. The restoring force exerted by the
spring on the mass will pull it towards to mean position. ‘O’.
Q.7 Define vibratory motion.
Answer: Vibratory Motion: A body is said to be vibrating if it moves back and forth or to and fro about a point. Another term for vibration is oscillation. A special kind of vibratory or oscillatory motion is called simple harmonic motion (SHM).
Q.8 Define SHM. Also write features of SHM.
Answer: Definition: Simple harmonic motion (SHM) occurs when the net force is directly proportional to the displacement from the mean position and is
always directed towards the mean position.
Features of SHM:
a. A body executing SHM always vibrates about a fixed position
b. Its acceleration is always directed towards the mean position.
c. The magnitude of acceleration is always directly proportional to its displacement from the mean position.
d. Acceleration will be zero at the mean position while it will be maximum at the extreme positions.
e. Its velocity is maximum at the mean position and zero at the extreme positions.
Q.9 . Define simple pendulum. Write down its time period equation/formula.
Answer: Definition: A simple pendulum is consist of a small bob of mass ‘m’ suspended from a light string of length T fixed at its upper end.
Time period equation :
Q.10 What is meant by vibration?
Answer: One complete round trip of a vibrating body about its mean position IS called one vibration.
Q.11 Define damped oscillations. Give its two examples for daily life.
Answer: Definition: The oscillations of system in the presence of some resistive force arc damped oscillations.
Examples:
(i) Shock absorbers in automobiles are one practical application of damped motion.
(ii) The motion of a pendulum is an example of damped motion.
Q.12 Define wave motion.
Answer: Wave motion: A wave is disturbance in the medium which causes the particles of the medium to undergo vibratory motion about their mean
position in equal intervals of time. The motion of wave is called wave motion.
Q.13 Define longitudinal waves.
Answer: Longitudinal Waves: In longitudinal waves the particles of the medium move back and forth along the direction of propagation of waves.
Q.14 Define Transverse Waves.
Answer: In case of transverse waves the vibratory motion of particles of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. e.g., waves on the surface of water.
Q. 15 Define electromagnetic waves. Also give an example.
Answer: Definition of Electromagnetic Waves: Waves which do not require any medium for their propagation are called electromagnetic waves.
Examples: Radio waves, Television waves, X-rays, heat and light waves are some examples of electromagnetic waves.
Q. 16 A ball is dropped from a certain height onto the floor and keeps bouncing. Is the motion of the ball is simple harmonic? Explain. Answer: No! The ball is dropped from a certain height it does not executing simple harmonic motion. Because during its bouncing it P.E. and time period is not
constant, more ever its amplitude is not constant.
Q.17 Define wave.
Answer: Wave: A wave is a disturbance in the medium which causes the particles of the medium to undergo vibratory motion about their mean position in equal
intervals of time.
Q.18 Define Crest and Trough.
Answer: Crest: The crests arc the highest points of the particles of the medium from the mean position.
Trough: The trough are the lowest points of the particles of the medium from the mean position.
Q.19 What is meant by compression?
Answer: Compression: Such a wave consists of regions called compression, where the loop of the spring are close together. In the regions of compression.
Particles of the medium are closer together.
Q.20 Define mechanical waves and give example.
Answer: Mechanical Waves: Waves which required any medium for their propagation are called mechanical waves.
Example:
- Waves produced on water surface.
- Sound waves
3. Waves produced in string and spring etc.
Q.21 What is difference between Mechanical Waves and Electromagnetic Waves?
Answer: Mechanical Waves: Waves which require any medium for their propagation called mechanical waves.
Examples: Waves produced in string etc.
Electromagnetic Waves: Waves which do not require any medium for their propagation are called
electromagnetic waves.
Examples: X-rays, radio waves etc.
Q.22 What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves?
Answer: Longitudinal Waves:
In longitudinal waves the particles of the medium move back and forth along the direction of propagation of wave.
Example: Sound, waves
Transverse Waves:
In case of transverse waves, the vibratory motion of particles of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves.
Example: Waves on the surface of water and light waves.
Q.23 Define diffraction of waves.
Answer: The bending or spreading of waves around the sharp edges or corners of obstacles or slits is called diffraction.
Q.24 Define reflection of waves.
Answer: Reflection of waves: When waves moving in one medium fall on the surface of another medium, they bound back into the first medium such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This process is called reflection of waves.
Q.25 State Hook’s law.
Answer: Hook’s law: “Within the elastic limit of the body. The applied force IS
directly proportional to the displacement.”
Mathematically
F ∝ x
F=-kx
Q.26 Define a time period. Write the formula of time period of a simple pendulum.
Answer: Time Period: The time taken by a vibrating body to complete one vibration is called time period.
Symbol: Time period represented by T.
Unit: The unit of time period is second (s).
Formula: ![]()
Time period is reciprocal of frequency i.e. T = 1/f
Q.27 Define frequency and write its unit.
Answer: Frequency: The number of vibrations or cycle of a vibrating body in one second is called is frequency.
Symbol: Frequency is represented by f.
Unit: Unit of frequency is Hertz (Hz).
Formula: Frequency is reciprocal of time period f = 1/T
Time period: The time taken by a vibrating. body to complete one vibration is called time period.
Unit: The T = 1/f