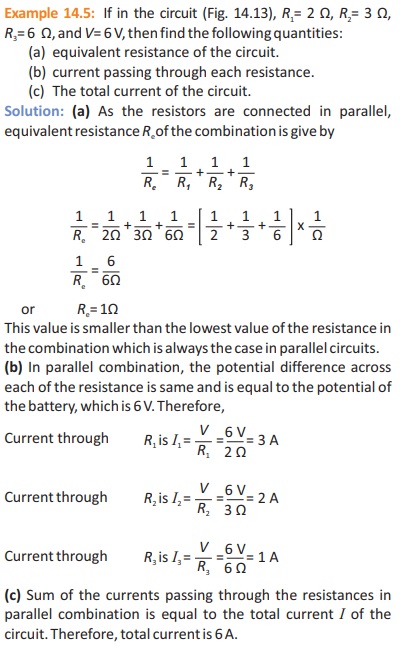
Chapter 14 Numerical Problems Examples
Example 14.1: If 0.5 C charge passes through a wire in 10 s, then what will be the value of current flowing through the wire?
Solution: Given that, Q = 0.5 C, t= 10 s, therefore by using
I = Q/t = 0.5 C/10 s=0.05 A= 50 mA
Example 14.2: Reading on voltmeter connected across a heating element is 60 V. The amount of current passing through the heating element measured by an ammeter is 2 A.
What is the resistance of the heating coil of the element?
Solution: Given that, V = 60 V, I = 2 A
Using Ohm’s law
V = IR
or R = V/I = 60V/2A 30 V A-1 = 30 Ω


Example 14.6: If a current of 0.5 A passes through a bulb connected across a battery of 6 for 20 seconds, then find V
the rate of energy transferred to the bulb. Also find the resistance of the bulb.
Solution: Given that, I = 0.5 A, V=6 V, t = 20 s
Now using the formula,
Energy W = VIt
we get, Energy = 6 V × 0.5 A × 20 s = 60 J
So the rate of energy transferred must be 60 J in 20 s or 3 J s-1 or 3 watt.
Now using, Energy = W = I2 Rt
We get resistance as
3 = (0.5)2 × R × 20
R = 3 ×1/20 × 1/0.25 = 3/5 = 0.6 Ω
Example 14.7: The resistance of an electric bulb is 500 Ω. Find the power consumed by the bulb when a potential difference
of 250 V is applied across its ends.
Solution: Given that, R = 500 Ω, V = 250 V
Using the formula, I = V/R
I = 250 V/ 500 = 0.5 A Ω
and Power P = I2 R = (0.5 A)2 × 500 Ω = 125 W
Example 14.8: Calculate the one month cost of using 50 W energy saver for 8 hours daily in your study room. Assume
that the price of a unit is Rs. 12.
Solution: Given that, Power = 50 W = 0.05 kW, time = 8 hours
Number of units consumed = 8 × 30 × 0.05 =12 units
Therefore, total cost = 12 × 12 = Rs. 144
<—————————–>