Unit 13 Electrostatics (Short Questions)
Q.1 Define charge.
Q.2 What is Electrostatic Induction?
Q.3 What is function of Electroscope?
Q.4 What is gold leaf electroscope?
Q.5 What is the numerical value of ‘k’ in Coulomb’s law?
Q.6 What is meant by point charge?
Q.7 Define electric field intensity. Write its SI unit.
Q.9 What is mean by Electric Field Line? What is its direction?
Q.10 Describe two properties of Electric Field Lines.
Q.11 Define electric field lines and electric potential.
Q.12 Define Electric Potential and give its mathematical equation.
Q.13 In which direction will positively charged particle move in an electric field?
Q.14 Define Capacitor and write its formula.
Q.15 In which form a capacitor stores energy?
Q.16 What is Dielectric in capacitor?
Q.17 Define Capacitance and state its SI unit.
Q.18 What is Electrolyte?
Q.19 What is meant by Filter circuit?
Q.21 Describe any two characteristics of series combination of capacitors.
Q.22 Why Electric bulb and Electric heater are not connected in series?
Q.23 Write the names of two types of capacitors and give one example on it.
Q.24 What is used as dielectric in paper Capacitors?
Q.25 Write two uses of capacitor.
Q.26 What are the hazards of static electricity?
Q.27 What is cause of lightening?
Q.28 Write the characteristics of charges.
Q.29 How charge is produced? Give an example.
Q.30 Describe the method of charging bodies by Electrostatic induction.
Q.31 How we can detect the type of charge by the use of electroscope?
Q.32 Define electric lines of force.
Q.33 In what direction will the positive charge move in an electric field?
Q.34 What is difference between Electric Field and Electric Intensity?
Q.35 Electric Intensity is a vector quantity. Why?
Q.36 Draw the electric field lines of a negative charge.
Q.37 Define the unit of electric field intensity.
Q.38 What is the relation between Electric Potential and Potential Energy?
Q.39 Describe the construction of capacitor.
Q.40 How a capacitor stores a charge? Explain.
Q.41 What is the difference between capacitor and dielectric?
Q.42 What is SI unit/unit of capacitance? Define.
Q.43 How many methods are there of combination of capacitors?
Q.44 On which factors does the ability of a Capacitor to store charge depends?
Q.45 Define fixed capacitor. Also give an example.
Q. 46 What do you know about Electrolytic Capacitors?
Q.47 Define mica capacitors and paper capacitors.
Q.48 Write down a brief note on application of electrostatics in spry painting.
Q.49 Write a brief note on electrostatic air cleaners.
Q.50 Describe two uses of electrostatics.
Q.1 Define charge.
Ans: Charge is a basic property of a material body due to which attracts or repels another object.
Charges are two types i.e. (i) Negative (ii) Positive
Q.2 What is Electrostatic Induction?
Ans: Electrostatic Induction: In the presence of a charge body, an insulated conductor develops positive charge at one end and negative charge at the other end. This process is called the electrostatic induction.
Q.3 What is function of Electroscope?
Ans: The gold leaf electroscope is a sensitive instrument used for detecting and testing the nature of charges on a body.
Q.4 What is gold leaf electroscope?
Ans: This is an instrument for detecting and measuring static electricity or voltage. A metal disc is connected to a narrow metal plate and a thin piece of gold leaf is fixed to the plate.
Q.5 What is the numerical value of ‘k’ in Coulomb’s law?
Ans: K is constant of proportionality. The value of k depends upon the medium between the two charges. If the medium between the two charges is air, then the value of k in Sl units will be (9 x 109 N m2/ C2).
Q.6 What is meant by point charge?
Ans: Point Charge: Coulomb’s law is true only for point charges whose sizes are very small as compared to the distance between them. The Columb’s Law applied for point charges.
Q.7 Define electric field intensity. Write its SI unit.
Ans: Electric field intensity: The electric field intensity at any point is defined as the force acting on a unit positive charge placed at that point. It is denoted by ‘E‘
OR
The strength of an electric field at any space is known as electric field intensity.
Unit: SI unit of electric intensity is NC-1.
Formula: Electric intensity can he determine from the following formula.
Q.8 Define Electric Field.
Ans: The electric field is a region around a charge in which it exerts electrostatic force on another charges.
Q.9 What is mean by Electric Field Line? What is its direction?
Ans: The direction of electric field intensity in an electric field line can also he represented by drawing lines. These lines are known as electric lines of
force. These lines were introduced by Micheal Faraday.
These pattern of lines, sometimes referred to as electric field lines, point in the direction that a positive test charge would accelerate if placed upon the line. As such, the lines are directed away from positively charged source charges and toward negatively charged source charges.
Q.10 Describe two properties of Electric Field Lines.
Ans: 1. Field lines never intersect each other.
2. They are perpendicular to the surface charge.
3. The field is strong when the lines are close together, and it is weak when the field lines move apart from each other.
4. The number of field lines is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge.
5. Field lines are always move away from positive charge towards negative charge.
6. The spacing between the field lines shows the strength of electric field.
Q.11 Define electric field lines and electric potential.
Ans: Electric Field Line: An electric field line is an imaginary line or curve drawn through a region of empty space so that its tangent at any point is in the direction of the electric field vector at that point. The relative closeness of the lines at some place gives an idea about the intensity of electric field at that point. These lines were introduced by Micheal Faraday.
Electric Potential: Electric potential at a point in an electric field is equal to the amount of work done to bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
Q.12 Define Electric Potential and give its mathematical equation.
Ans: Electric potential at a point in an electric field is equal to the amount of work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
Mathematical Equation: If W is the work done in moving a positive charge q from infinity to a certain point in the field. The electric potential
V at this point would be given by V = W / Q
Q.13 In which direction will positively charged particle move in an electric field?
Ans: A body in gravitational field always tends to move from a point of higher potential energy to a point of lower potential energy. Similarly. when a positive charge is released in an electric field, it moves from a point of higher potential to lower potential.
Q.14 Define Capacitor and write its formula.
Ans: Capacitor: A device used for storing electric charges is called capacitor.
Formula: Potential difference is directly proportional to the charge Q deposited on the plate.
Q.15 In which form a capacitor stores energy?
Ans: Capacitor stores energy in an electric field between two plates in the form of electrostatic potential energy.
Q.16 What is Dielectric in capacitor?
Ans: Dielectric: In Capacitors the medium between the two plates is air or a sheet of some insulator. This medium is known as dielectric.
Q.17 Define Capacitance and state its SI unit.
Ans: Capacitance: The ability of the capacitor to store charge Is called capacitance. The capacitance of a capacitor is a ratio between charge and potential difference.
Symbol: It is denoted by ‘C’
Formula: C = Q / V
Q.18 What is Electrolyte?
Ans: Electrolyte: Those substance that conducts electric current as a result of dissociation in to positively and negatively charged particles called ions. Which discharged at negative and positives terminal. The most familiar electrolytes are acids, bases and salts.
Q.19 What is meant by Filter circuit?
Ans: Capacitor can be used to differentiate between high frequency and low frequency signals such circuit is called Filter circuit.
Q.20 What is the effect of increasing area of capacitors plates on the charge storing capacity of capacitors?
Ans: When the area between two plates of capacitors is increased then the capacity of a capacitor increases.
Q.21 Describe any two characteristics of series combination of capacitors.
Ans: Characteristics of series combination of capacitors:
i) Each capacitor has the same charge across it.
ii) The potential difference across each capacitor is different due to different values of capacitance.
Q.22 Why Electric bulb and Electric heater are not connected in series?
Ans: It is impracticable to connect an electric bulb and an electric heater in series because it will divide the voltage.
Q.23 Write the names of two types of capacitors and give one example on it.
Ans: Types of Capacitors
- Fixed Capacitor: A capacitor in which the area between two plates cannot change i.e paper capacitor is the example of fixed capacitor.
ii. Variable Capacitor: In variable type of capacitors some arrangement is made to change the area of the plates facing each other. Capacitor used in radio
tuning.
Uses: Variable capacitors are usually utilize or tuning in radio sets.
Fixed Capacitors
i) Area of plates can’t be changed.
ii) In general, oil greace, paper or plastic sheet is putted between aluminum foil is used as dielectric.
iii) It is packed in cylindrical shaped strong coding.
Variable Capacitors
i) Area of plates can be changed.
ii) Air is used as dielectric material.
It consists of set of plates one plate is variable and other is fixed.
Q.24 What is used as dielectric in paper Capacitors?
Ans: Usually, an oiled or greased or as thin plastic sheet is used as a dielectric between two aluminium foils in paper capacitors.
Q.25 Write two uses of capacitor.
Ans: Capacitors have wide range of application in different electrical and electronic circuits.
- They are used for tuning transmitters, receivers and transistor radios.
2. They are also used for table fans, ceiling fans, exhaust fans, fan motors in air conditioners.
3. Capacitors are also used in electronic circuits of computers.
4. Capacitors can be used to differentiate between high frequency and low frequency signals.
Q.26 What are the hazards of static electricity?
Ans: i) A fire or an explosion may occur due to excessive build-up of electric charges produced by friction or clouds. If static charges are allowed to discharge through the areas where there is petrol vapour a fire can occur.
Q.27 What is cause of lightening?
Ans: The phenomenon of lightening occurs due to a large quantity of electric charge which builds up in the heavy thunderclouds. The thunderclouds are charged by friction between the water molecules in the thunderclouds and the air molecules. When the charge on the thunderclouds is sufficiently high, it can produce positive and negative charges in the air. The huge amount of negative charge is discharged to the highest object on the ground and can harm them.
Q.28 Write the characteristics of charges.
Ans: Characteristics of charges:
- Charge is a basic property of a material body due to which it attracts or repels another objects.
- Friction produces two different types of charges on different material.
- Like charges always repel each other:
- Unlike charges always attract each other.
- Repulsion is the sure test of charge on a body.
Q.29 How charge is produced? Give an example.
Ans: A charge can be produced by rubbing one neutral body to other neutral body due to friction.
Example: By rubbing plastic rod with fur, the charge will produce on plastic rod.
Q.30 Describe the method of charging bodies by Electrostatic induction.
Ans: “If in the presence of a charged body, an insulated conductor develops positive charge at one end and negative charge at the other end, this process is called the electrostatic induction.” This method to use charging bodies.
Q.31 How we can detect the type of charge by the use of electroscope?
Ans: In order to detect the type of charge on a body, bring the charged body near the disk of the positively charged electroscope. If the divergence of the leaves increase, the body carries positive charge, if the divergence decreases the body has negative charge. If the body is neutral there will he no deflection of the leaves.
Q.32 Define electric lines of force.
Ans: Electric lines: The direction of electric field intensity in an electric field can also be represented by drawing lines. These lines are known as electric lines of force.
Q.33 In what direction will the positive charge move in an electric field?
Ans: “If the test charge is free to move, it will always move in the direction of electric intensity.”
Q.34 What is difference between Electric Field and Electric Intensity?
Ans: Electric Field: The electric field is a region around a charge in which it exerts electrostatic force on another charges.
Q.35 Electric Intensity is a vector quantity. Why?
Ans: Electric Intensity: The strength of an electric field at any point in space is known as electric field intensity.
Q.36 Draw the electric field lines of a negative charge.
Ans: Due to negative charge the direction of electric field lines always in to the paper.
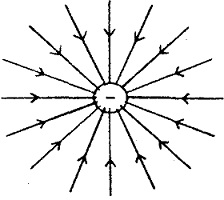
Q.37 Define the unit of electric field intensity.
Ans: Unit of electric field intensity: The SI unit of electric field, intensity is Newton per Coulomb (NC-1).
Electric field intensity: The electric field intensity at any point is define as if one Newton force acts on 1 Coulomb charge then its electric field intensity is 1 Newton per coulomb (NC-1)
Q.38 What is the relation between Electric Potential and Potential Energy?
Ans: A body in gravitational field always tends to move from a point of higher potential energy to a point of lower potential energy. Similarly, when a charge is released an art electric field, it moves from a point of higher potential say A to a point at lower potential say B.
Q.39 Describe the construction of capacitor.
Ans: Construction of Capacitor: Capacitor consists of two thin metal plates, parallel to each other separated by a very small distance. The medium between the two plates is air or a sheet of some insular.
Q.40 How a capacitor stores a charge? Explain.
Ans: If a capacitor is connected to a battery of V volts, then the battery transfers a charge +Q from plate B to plate A, so that -Q charge appears on plate B and +Q charge appears on plate A. The charges on each plate attract each other and thus remained bound with in the plates.
Q.41 What is the difference between capacitor and dielectric?
Ans: Capacitor: A device which is used to store electric charge is called capacitor.
Dielectric: In capacitors, the medium between the two plates is air or a sheet of some insulator. This medium is known as dielectric.
Q.42 What is SI unit/unit of capacitance? Define.
Ans: The S.I unit of Capacitance is Farad (F).
Farad: If one coulomb of charge given to the plates of a capacitor produces a potential difference of one volt between the plates of the capacitor then its capacitance would be one Farad.
Q.43 How many methods are there of combination of capacitors?
Ans: There are two methods for combination of capacitors:
i) Parallel combination ii) Series combination
Q.44 On which factors does the ability of a Capacitor to store charge depends?
Ans: Three factors affects the ability of capacitors to store charge.
i) Area of the plates ii) Distance between the plates
iii) Types of insulators is used between the plates
Q.45 Define fixed capacitor. Also give an example.
Ans: Fixed Capacitor: A capacitor in which the area between two plates cannot change is called fixed capacitor.
Example:
- Paper capacitor is the example of fixed capacitor.
- Mica capacitor is the example of fixed capacitor.
Q. 46 What do you know about Electrolytic Capacitors?
Ans: Electrolytic capacitor: Electrolytic capacitor is consists of a metal foil in contact with an electrolyte a solution that conducts charge by virtue of the
motion of the ions contained in it. When a voltage is applied between the foil and the electrolyte, a thin layer of metal oxide (an insulator) is formed on the foil, and this layer serves as the dielectric. Very large capacitance can be attained because the dielectric layer is very thin.
Q.47 Define mica capacitors and paper capacitors.
Ans: Mica Capacitors: It is example of fixed capacitors in which mica is used as dieletive material. For safety packed into plastic hole.
Paper Capacitors: It is also example of fixed capacitors where oil or greace or paper or plastic is used as diercctric two aluminium foils.
Q.48 Write down a brief note on application of electrostatics in spry painting.
Ans: Automobile manufacturers use static electricity to paint new cars. The body of a car is charged and then the paint is given the opposite charge by charging the nozzle of the sprayer. The charged paint particles are
attracted to the car and stick to the body just like a charged balloon sticks
to a wall. This is a very effective. efficient and large seak.
Q.49 Write a brief note on electrostatic air cleaners.
Ans: Electrostatic air cleaners: An electrostatic air cleaner is used in homes to relieve the discomfort of allergy sufferers Air mixed with dust and pollen enters the device across a positively charged mesh. The airborne particles become positively charged when they make contact with mesh. The electrostatic force of attraction between the positively charged particles in the air and the negatively charged mesh causes the particles to precipitate out on the surface of the mesh. Through this process we can remove a very high percentage of contaminants from the air stream.
Q.50 Describe two uses of electrostatics.
Ans: Static electricity has an important place in our daily life which include photocopying, car painting, extracting dust from dirty carpets and from chimneys of industrial machinery.
Uses of electrostatics are given below:
- An electrostatic air cleaner is used in homes to relieve the discomfort of
allergy sufferers. - Automobile manufacturers use static electricity to paint new cars.