Unit 16 Basic Electronics (Short Questions)
Q.1 What is meant by thermionic emission?
Q.2 Name two factors which can enhance thermionic emission.
Q.3 How are the electrons deflected by electric field?
Q.4 What is meant by Cathode Ray Oscilloscope?
Q.5 For which purpose electron gun is used in oscilloscope?
Q.6 Define OR operation and write its Boolean equation.
Q.7 How the filament is heated-in an oscilloscope and why it is heated?
Q.8 Define digital quantities and give examples.
Q.9 What is relation between Digital Quantities and Digital Electronics?
Q.10 Describe the uses of Digital Electronics.
Q.11 Differentiate between digital and analogue quantities.
Q.12 What is meant by electronics?
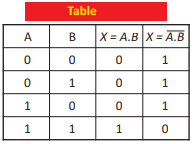
Q.13 Write truth table of OR operation.
Q.14 What is meant by Logic States?
Q.15 What is meant by Boolean algebra? How it is represented?
Q.16 Draw the circuit diagram of AND operation.
Q.17 Make the symbol diagram and Truth Table and AND gate.
Q.18 Which gate performs logical complementation? Draw its logical symbol.
Q.19 What is NAND gate? Write its truth table.
Q.20 Define electronics.
Q.21 Differentiate between analogue and digital quant.
Q.22 Draw symbol for NOR gate and write its truth table.
Q.23 Give two reasons to support the evidence that cathode rays are negatively charged.
Q.24 Shortly explain the deflection of electrons by magnetic field.
Q.25 Write down the two uses of cathode ray oscilloscope.
Q.26 Define digital electronics.
Q.27 What is meant by ADC and DAC?
Q.28 Write the names of basic operation of digital electronics.
Q.29 What are the three Universal Logic Gates?
Q.30 What is meant by AND operation? Draw the diagram of AND gate.
Q.31 Define truth table.
Q.32 How can you compare the logic operation X = A. B with usual operation of multiplication?
Q.33 Write the truth table of OR gate and also draw their circuit diagram.
Q.34 What do you mean by fluorescent screen?
Q.35 What is NOT gate? Draw its symbol.
Q.37 What is meant by Logic Operation? Write its two kinds.
Q.38 What is meant by binary variable?
Q.39 Draw diagram of NAND gate and write its truth table.
Q.40 How NAND gate is made? Write symbolic representation of NAND gate.
Q.41 NAND gate is the reciprocal of AND gate. Discuss briefly.
Q.42 Explain NOR gate. Draw its symbol.
Q.43 Make the Truth Table for NOR Gate.
Q.44 State mathematical formula of NOR gate.
Q.1 What is meant by thermionic emission?
Ans: Thermionic Emission: The process of emission of electrons from the hot metal surface is called thermionic emission.
Q.2 Name two factors which can enhance thermionic emission.
Ans: Thermionic emission depends upon the following factors .
- i) Temperature ii) Voltage iii) Nature of metal
Thermionic emission increases with the increase in temperature and voltage .
Q.3 How are the electrons deflected by electric field?
Ans. When we pass a beam of electrons into an electric field, they deflect to the positive plate, due to which positive charges present in the plates attract electrons and negative charges repel these electrons, due to which electrons deflects by electric field.
Q.4 What is meant by Cathode Ray Oscilloscope?
Ans. Cathode Ray Oscilloscope: Cathode-ray oscilloscope is an instrument which is used to display the magnitudes of changing electric currents or potentials in form, of graphs: C.R.O stands for CATHODE RA Y OSCILLOSCOPE.
Q.5 For which purpose electron gun is used in oscilloscope?
Ans: Electron gun in oscilloscope is used to produce a fine beam of electrons.
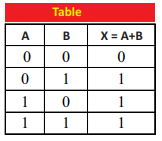
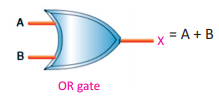
Q.6 Define OR operation and write its Boolean equation.
Ans. OR Operation: The operation whose output is off (0) when all inputs are closed (0) otherwise output is open (1).
Boolean Equation: X = A + B
Truth Table:
Ans. The filament is connected.to a 6 volt external battery. When it is heated a large number of electrons are free to move. The more negative this potential, the more electrons will be repelled from the grid and hence fewer electrons will be reached the anode and the screen.
Q.7 How the filament is heated-in an oscilloscope and why it is heated?
Ans: The filament is connected.to a 6 volt external battery. When it is heated a large number of electrons are free to move. The more negative this potential, the more electrons will be repelled from the grid and hence fewer electrons will be reached the anode and the screen.
Q.8 Define digital quantities and give examples.
Ans. Digital Quantiles: The quantities whose values vary in non-continuous manner are called digital quantities.
Example: The use of digital electronics was limited to computer only but nowadays its application is very wide spread i.e. Modern telephone system, radar system, naval and other system of military importance use of digital quantities.
Q.9 What is relation between Digital Quantities and Digital Electronics?
Ans. Digital Quantities
The quantities whose values vary in non-continuous manner are called digital quantities.
Digital Electronics: The branch of electronics which deals with digital quantities is called digital electronics.
Q.10 Describe the uses of Digital Electronics.
Ans: Uses of Digital Electronics: Modern telephone system. radar system, naval and other systems of military importance, devices to control the operation of industrial machines, medical equipment’s and many household appliances are using digital technology.
Q.11 Differentiate between digital and analogue quantities.
Ans: Digital Quantities: The quantities whose values vary in non-continuous manner are called digital quantities.
Analogue Quantities: The quantities whose values vary continuously or remain constant known as analogue quantities.
Q.12 What is meant by electronics?
Ans. Digital Electronics: The branch of electronics which deals with digital quantities is called digital electronics, Digital electronics use only two digital 0 (zero) and 1 (one) and whole data is provided in binary form.
Q.13 Write truth table of OR operation.
Ans.
Truth Table:

Q.14 What is meant by Logic States?
Ans: Logic States: The states of Boolean variables’ are called logic states. These are 0’s or 1’s. This condition is called logic states.
Q.15 What is meant by Boolean algebra? How it is represented?
Ans: Boolean algebra
The algebra which is used to describe the logic operations by means of symbols (A,B,C. .. ) is called Boolean algebra. It is represented by using Boolean variable i.e. 1’s or 0’s.
Q.16 Draw the circuit diagram of AND operation.
Ans:
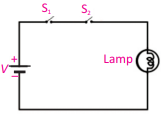
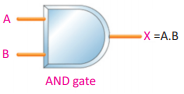
Q.17 Make the symbol diagram and Truth Table and AND gate.
Ans. AND gate: The circuit which implements the AND operation is known as AND gate.

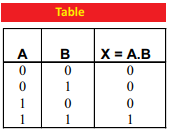
Q.18 Which gate performs logical complementation? Draw its logical symbol.
Ans. Logical Complementation: NOT gate performs logical complementation. NOT gate performs the basic logical function called inversion or complementation. NOT gate is also called inverter.
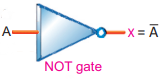
The purpose of this gate is to’ convert one logic level into the opposite logic level.
Q.19 What is NAND gate? Write its truth table.
Ans. NAND gate: NAND gate is obtained by coupling NOT gate with the output terminal of the AND gate. The electronic circuit which implements NAND operation is known as NAND gate.
Symbol:
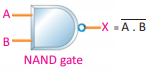
Truth Table
Ans. Electronics: Electronic is that branch of applied physics which deals with the control of motion of electrons using different devices. Electronic devices being more effective. arid reliable have revolutionized. The field of telecommunication and information technology.
Q.21 Differentiate between analogue and digital quant
Ans. Analogue Electronics
The branch of electronics. consisting of, circuit which process analogue quantities is called analogue electronics.
Analogue Quantities:
The quantities whose values vary continuously or remain constant are known as analogue quantities.
Q.22 Draw symbol for NOR gate and write its truth table.
Ans.
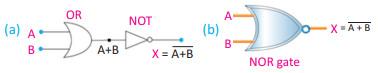
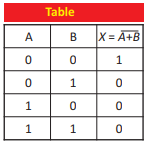
Q.23 Give two reasons to support the evidence that cathode rays are negatively charged.
Ans. i) In the electric field, cathode rays deflects towards the positive plate.
ii) In cathode ray tube (CRT), cathode rays travels in the opposite direction of cathode terminal.
These reasons prove that cathode rays are negatively charged.
Q.24 Shortly explain the deflection of electrons by magnetic field.
Ans. When we apply magnetic field at right angle to the beam of electron by using a horseshoe magnet we observe that the spot of the electron beam on the screen is deflected from the original position. If the change the direction of magnetic field the direction of deflection of electrons will also change.
Q.25 Write down the two uses of cathode ray oscilloscope.
Ans. Uses of cathode ray oscilloscope
The CRO is used in many fields of science.
Q.26 Define digital electronics.
Ans. Analogue Electronics: The branch of electronics consisting of circuits which process analogue quantities is called analogue electronics.
Q.27 What is meant by ADC and DAC?
Ans. ADC
The circuit which converts the analogue signal into a digital one in the form of digits is called analogue to digital converter, (ADC).
DAC: The circuit which converts a digital signal into an analogue signal is called digital to analogue converter, (DAC).
Q.28 Write the names of basic operation of digital electronics.
There are three basic operations of digital electronics.
i) AND operation ii) OR operation iii) NOT operation
Q.29 What are the three Universal Logic Gates?
Ans. They are
i) AND gate ii) OR gate iii) NOT gate
Q.30 What is meant by AND operation? Draw the diagram of AND gate.
Ans. AND Operation: Such a logic operation whose value is I only when it’s all inputs are at 1 is called AND operation.

Ans. Truth Table: Set of inputs and outputs in binary form is called truth table.
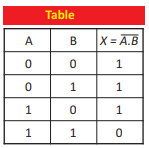
Q.32 How can you compare the logic operation X = A. B with usual operation of multiplication?
Ans. Logic operation X = A. B is called “AND Operation”. Its truth table is:

As in ordinary multiplication, multiplication by zero is zero and the multiplication of non-zero numbers gives a non-zero number. Similarly, in AND gate, if one switch is open (0) then lamp will remain OFF (0). The lamp will bright/ON (1) when both switches are ON (1).
Q.33 Write the truth table of OR gate and also draw their circuit diagram.
Ans: OR gate
The electronic circuit which implements the OR operation is known as OR gate.
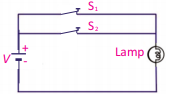

Q.34 What do you mean by fluorescent screen?
Ans. Fluorescent screen
The screen of a cathode ray oscilloscope consists of a thin layer of phosphorus, which is a material that gives light as a result of bombardment by fast moving electrons. This screen appears. as a circular or rectangular window usually with a centimeter graph superimposed on it.
Q.35 What is NOT gate? Draw its symbol.
Ans. NOT Gate: The electronic circuit which implements NOT operation is known as NOT gate.

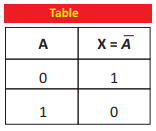
Ans. NOT Operation: The operation that invert the input is called ‘NOT’ operation’. It is also known as inversion.
Truth Table

The circuit which implements the NOT operation is known as NOT gate.
Diagram:

Q.37 What is meant by Logic Operation? Write its two kinds.
Ans: Logic Operation:
Different operations of Boolean variables are called logic operations.
i) OR-Operation ii) AND-Operation iii) NOT-Operation
Q.38 What is meant by binary variable?
Ans: Binary Variable: Such things which can only two possible states are known as binary variables. The states of binary variable are usually represented by the digits 0 and 1. Here 0 (zero) means off or False and 1 (one) means On or True.
Q.39 Draw diagram of NAND gate and write its truth table.
Ans:
Symbol:

Truth Table

Q.40 How NAND gate is made? Write symbolic representation of NAND gate.
Ans. When the output of AND gate is connected with input NOT gate we obtained NAND gate.
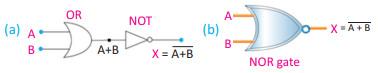
Q.41 NAND gate is the reciprocal of AND gate. Discuss briefly.
Ans. AND Gate: A gate whose output is ON (I) when it’s 1:111 inputs are ON
(1) otherwise output is OFF (0).
Boolean Expression: X = A. B
NAND Gate: A gate whose output is OFF (0) when it’s all inputs are ON
(1) otherwise input is ON (1).
Boolean Expression: ![]()
Truth Table
Q.42 Explain NOR gate. Draw its symbol.
Ans. NOR Gate: The NOR gate is obtained by coupling the output of the OR gate with the NOT Gate.
Equation: ![]()
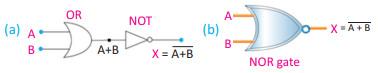
Q.43 Make the Truth Table for NOR Gate.
Ans:

Q.44 State mathematical formula of NOR gate.
Ans. Mathematical formula of NOR gate is: X = A + B
The NOR gate is obtained by coupling the output of the OR gate with NOT gate.