Unit 3 – Networks (Exercise Questions)
3.3. Write short answers.
Q.1. How client and server communicate with each other?
Q.2. What are the main components of communication?
Q.3. How telephone addressing relate with network addressing?
Q.4. What is difference between static and dynamic IP?
Q.5. Define communication channel.
Q.6. Describe the working of web browser.
Q.7. What is the difference between point-to-point and multipoint connection?
Q.8. What is application sharing? Answer with the help of an example.
Q.9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of star topology over bus topology?
Q.10. In a client server model, is client software or hardware? Give reasons to support your answer.
3.4. Answer the following questions.
Q.1. What is network topology? Describe bus, star, ring and mesh topologies with e diagram of each.
Q.2. What is TCP/IP? Describe its five layers with their functions.
Q.3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of star topology over bus topology?
Q.4. What are the sizes of IPv4 and IPv6? Explain the method to calculate the size of these both standards.
Q.1. How client and server communicate with each other?
Answer:
Server
The server is a computer that provides services to other computers and devices connected to the network. The server controls access to the hardware, software and other resources on the network. It also provides centralized storage area for programs, data and information. Servers usually have more processing power, memory and hard disk space than clients.
Some servers are known as dedicated servers. Different types of dedicated servers include file server, print server, database server and web server. A dedicated server is used to perform a specific task. For example, file server is used to store and manage files. Print server is used to manage printers and print jobs.
Client
The client is a computer in the network that is connected with a server to access different resources. The client sends request to server for resources. The server provides requested resource to client. The client is typically less powerful than server.
In general, a client is a hardware device. A cell phone, laptop and desktop computer is a client. The client application is a software that is used to send a request from client to server. It provides an interface to send the request to the server. Web browser is an example of a client application.
Client/Server Communication
The communication between client end server is based on request and response. The client sends request to the server for resources. The server provides the requested resource to client. For example, a server may store the company’s email messages, The clients on the network access email messages on the server. The clients may be any user connected to the network using the computers or mobile devices. The client provides username and password to login. The server provides access to the email account after verifying the username and password.
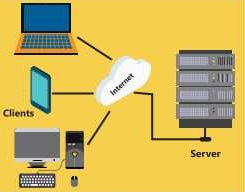
Figure: Client-Server Communication
Q.2. What are the main components of communication?
Answer:
Data Communication
Data communication is the exchange of messages between sending and receiving devices through a communication medium. The messages are the information that may be in the form of text, numbers, images, audio and video.
Components of Data Communication
A data communication system consists of hardware and software to transfer data from one place to another. Different components of data communication system are as follows:
1. Sender
Sender is a device that sends the message. It initiates communication process. It is also called source or transmitter. A computer is normally used as sender in data communication systems .
2. Receiver
Receiver is a device that receive the message. It is also called sink. The receiver must be capable of accepting a message. The receiver can be computer, printer or another computer related device.
3. Message
The message is the data, information or instruction to be communicated. It may consist of text, number, picture, audio, video or a combination of these.
4. Protocol
A protocol is a set of rules that governs data communication. It is a formal agreement between communication devices to send and receive information. The devices cannot communicate without protocol.
5. Transmission Medium
Medium is the path that connects sender and receiver. It is used to transmit data. It is also called communication channel. The transmission medium can be wired or wireless. The wired transmission media are twisted pair cable, coaxial cable and fiber optic cable. The wireless transmission media include radio waves, microwaves and satellites etc. A device may have multiple transmission channels at a time. For example, mobile phone connected to the Internet uses data channel (3G, 4G, LTE) to access Internet. It uses voice channel for making calls.
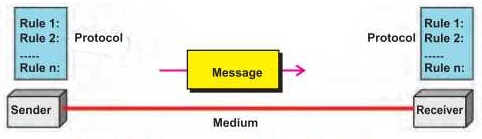
Figure: Components of data communication
Q.3. How telephone addressing relate with network addressing?
Answer:
Mapping between Telephone & Network Addressing
IP address acts as a telephone number. Suppose a user needs to call another person. The telephone number is required to make the call. Similarly, a device uses the IP address of the other device to communicate with it.
Each device connected to the Internet has an IP address. All IP addresses are unique like the telephone numbers. All devices communicate with other devices using the IP addresses. The IP addresses can be static or dynamic.
Static IP Address
Static IP address is a type of IP address that remains the same every time the device is connected to the Internet. The server uses static IP address.
Dynamic IP Address
Dynamic IP address is a type of IP address that is assigned each time a device is connected to the Internet. The user computers typically use dynamic IP address.
Q.4. What is difference between static and dynamic IP?
Answer:
Static IP address is a type of IP address that remains the same every time the device is connected to the Internet. Dynamic IP address is a type of IP address that is assigned each time the device is connected to Internet.
Q.5. Define communication channel.
Answer:
The message in data communication is sent in the form of packets, Each message consists of two parts called payload and control information.
1. Payload
Payload is the actual contents of the message. Suppose a user writes an email message to a friend. The content of the email message is the payload.
2. Control Information
Control information contains the information about the sender and the receiver. It is also called header of the message. The control information is used to deliver the message to the receiver properly. The message cannot be delivered if the control information is wrong or missing.
Example
Suppose a school sends the result cords of all students to their home addresses. In this example, the detail on the result card is the payload. The address on the envelope is the control information. It will be used to deliver the result card to the related student.
Q.6. Describe the working of web browser.
Answer:
Web browsers are used to access the World Wide Web. Web browsers and Web servers function together as a client-server system. As a client/server model, the browser is the client run on a computer that contacts the Web server and requests information. The Web server sends the information back to the Web browser. The web browser displays the results on the computer or other Internet-enabled device that supports a browser.
Q.7. What is the difference between point-to-point and multipoint connection?
Answer:
A point-to-point connection refers to direct link between a sender and a receiver. Both devices are connected with one connection line. A multipoint connection refers to the link between one sender and multiple receivers. A single link can be shared by more/devices.
Q.8. What is application sharing? Answer with the help of an example.
Answer:
Application Sharing
The individual licensed copy of application software can be costly. The application can be shared over a network among many users to save a lot of money. In this case, the user does not need to purchase separate copy of the
application for each computer. For example, the manager, cashier and ATM user use the same application. The bank balance of a user updated in one branch is shown in all branches immediately.

Figure: Application Sharing
Q.9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of star topology over bus topology?
Answer:
The advantages are that star topology is more reliable than bus topology. It is easy to manage and maintain than bus topology. The disadvantages are that it consumes more cable than bus topology. It is more expensive to implement than bus topology.
Q.10. In a client server model, is client software or hardware? Give reasons to support your answer.
Answer:
In general, a client is a hardware device. A cell phone, laptop and desktop computer is a client. However, the software running on that hardware makes it a client.
3.4. Answer the following questions.
Q.1. What is network topology? Describe bus, star, ring and mesh topologies with e diagram of each.
Answer:
Network Topology.
A network can be arranged in different ways, The physical layout or arrangement of connected devices in a network is called network topology. It is the shape of a network. Different network topologies are as follows:
- Bus Topology
- Ring· Topology
- Star Topology
- Tree Topology
- Mesh Topology
Bus Topology
Bus topology is the simplest type of network, It supports a small number computers. In bus topology, all computers or devices are connected to a common communication medium. This medium is known as bus or backbone. The terminators are used at the end of a bus to absorb signals and stop them to travel backwards.
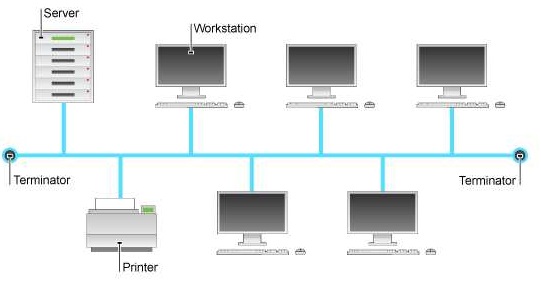
Figure: Bus topology
Working of Bus Network
The sending computer sends the data and destination address through the bus. The data and address move from one computer to the other in the network. Each computer checks the address. If it matches with the address of a computer, the computer keeps the data. Otherwise the data moves to the next computer.
Advantages
- It is simple and easy to use.
- It requires small length of cable to connect computers.
- It is less expensive.
- If one computer fails, it does not affect the rest of the network.
Disadvantages
- It only supports small number of computers.
- The network speed slows down as the number of computers increases.
- The entire network stops working if there is a problem in the central cable.
Star Topology
All computers in star topology are connected to a central device called switch or hub with point to point link. Point to point link means there is dedicated link or cable between two devices. Other devices cannot use it. Star topology is mostly used in the client-server networks.
Working of Star Network
The sending computer sends the data to the central device. The central device sends data to the receiving computer. Each computer in star network communicates with the central device.
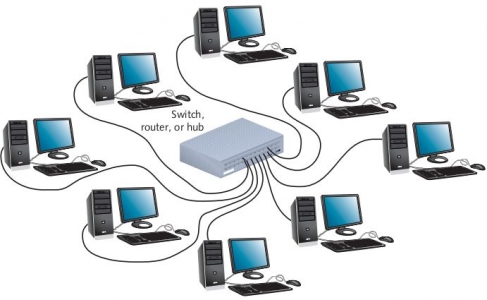
Figure: Star topology
Advantages
- It is easy to manage and modify network.
- Adding or removing computers can be done without disturbing the network.
- Finding faults become very simple.
Disadvantages
- If central device such as hub or switch fails, the entire network breaks down.
- It requires a Large length of cable.
- It is more expensive.
Ring Topology
In ring topology, each computer is connected to the next computer with the last one connected to the first. A ring of computers is formed in this way. A ring co be unidirectional or bidirectional. In a unidirectional ring topology, data can be sent in one direction. It can be either clockwise or anticlockwise. In a bidirectional ring topology, data can travel in any direction.
Working of Ring Network
Every computer is connected to next computer in a ring. Each compute receives message from the previous computer and transmits it to the next computer. The message is passed from one computer to other until it reaches the correct destination computer.
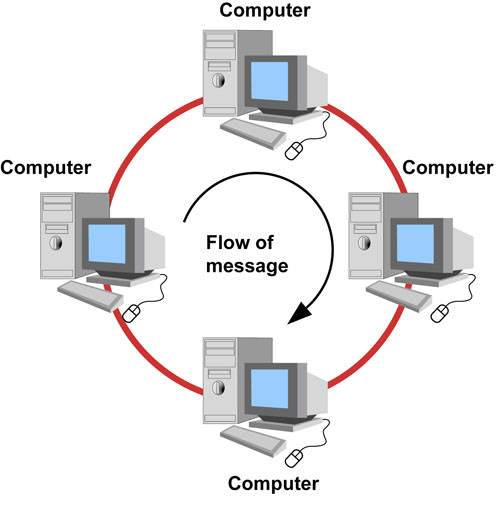
Figure: Ring topology
Advantages
- It is less expensive than star topology.
- Every computer has equal access to the network.
Disadvantages
- Failure of one computer in the ring can disable the whole network.
- Adding new computer or removing existing computer affects the network.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every device in the network is physically connected to every other device in the network. A message can be sent on different possible paths from source to destination more quickly. Mesh topology provides improved performance and reliability.
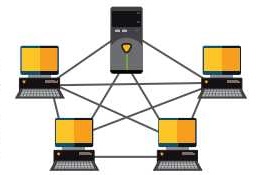
Figure: Mesh topology
Advantages
- The network continue working if one device on the network fails.
- It is more secure as the data remains between sender and receiver.
- It is more reliable as it provides point-to-point connection between two device
Disadvantages
- Mesh technology is expensive as it uses a lot of wires.
- It is difficult to install and modify.
Q.2. What is TCP/IP? Describe its five layers with their functions.
Answer:
Computer Networks Models
Network model is used to manage the communication between computers on a network. A network model uses different layers to carry out communication. Each layer is used to perform different functions. Two popular types of network models are TCP/IP and OSI.
TCP/IP
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol I Internet Protocol. TCP/IP is a network model that is used to transfer data from one computer to another over the Internet and other networks.
Layers in TCP/IP
TCP/IP model consists of five layers. Each layer usually has more than one protocols to carry out the functions. Each layer receives’ data from the layer above it. It adds some control information to the data known as header. The actual content of the message is hidden inside the header at each layer. This is called encapsulation.
Different layers in TCP/IP model are as follows:
1. Application Layer
The application layer is the top most layer of TCP/IP model. It provides an interface between network services and application programs. The users mostly interact with this layer. Many protocols are used at this layer to perform various functions. All these protocols collectively form the application layer. These protocols form the basics of various network services such as user login, file transfer, web surfing and email etc. FTP, HTTP and SMTP are some’ examples of protocols used at application layer.
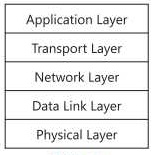
Figure: The layers in TCP/IP model
2.Transport Layer
The transport layer provides the mechanism to transport data between network devices. It controls the flow of data. It ensures that messages are delivered without any error. It divides large messages into small segments for efficient transmission. Th transport layer also provides the acknowledgement of successful data transmission.
The data is retransmitted if there are any error’s in the transmission. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is an example of protocol used at transport layer.
3. Network Layer
The network layer manages the delivery of data from source to destination across different networks. There may be many networks between two computers. This layer manages to send data from source computer to the destination computer. The network layer ‘finds the best physical path for the data to reach its destination. This process is called routing. internet Protocol (IP) is an example of protocol used at network layer.
4. Data Link Layer
The data link layer manages the transfer of data between the devices on the same network. It also manages the flow and error control of data. It detects and retransmits faulty data. The protocol of this layer determines which device has control over the link at any given time when two or more devices connect to the same link Ethernet is an example of protocol used at data link layer.
5. Physical Layer
The physical layer is the bottom layer of TCP/IP model. This layer is about the transmission media used in communication such as cables or wireless connection. It defines the data transmission rate in terms of number of bits sent per second.
Q.3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of star topology over bus topology?
Answer:
The advantages are that star topology is more reliable than bus topology. It is easy to manage and maintain than bus topology. The disadvantages are that it consumes more cable than bus topology. It is more expensive to implement than bus topology.
Q.4. What are the sizes of IPv4 and IPv6? Explain the method to calculate the size of these both standards.
Answer:
IPv4
The original IPv4 protocol is still used today on both the Internet and many business networks. IPv4 is a 32-bits (232) in size. It provides approximately 4.3 billion addresses. The 32 bits are divided into four parts known as octet. One octet is equal to 8 bits. The four octets are separated by dot. Each octet in the IP address is written in decimal format. Each octet can contain a decimal value from 0 to 255.
Example
The following example shows an IPv4 address:
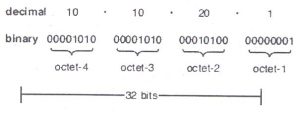
Figure: Structure of IPv4 address
IPv6
Many devices are connecting to the Internet. It was a concern that IPv4 may not be enough for all these devices. IPv6 was introduced as a solution for expanding the possible number of users on the Internet. It was developed by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It became draft standard in December 1998 and Internet Standard in 14 July 2017.
IPv6 is a 128-bits (2128) in size. It provides approximately 3.4×1038 addresses. It is 7.9 x 1028 times more than the number of addresses in IPv4. IPv6 is written in hexadecimal. It has eight groups separated by colon (:). Each group has four hexadecimal digits. One hexadecimal digit needs 4 bits and a group of four hexadecimal digits needs 16 bits. IPv6 address has eight groups of 16 bits so one address needs 128 bits.
Example
An example of IPv6 address is as follows:
2DAB:FFFF:0000:3EAE:01 AA:00FF:DD72:2C4A