Q.5 What is Fermentation and write down its types.
Answer:
Cellular respiration
In cellular respiration glucose molecule goes through oxidation reduction reactions to release energy in the form of ATP.
Fermentation
Fermentation is the process in which there is incomplete oxidation – reduction of glucose.
Fermentation has been in the knowledge of man since centuries but it was believed that it is purely a chemical process.
Louis Pasteur and Fermentation
In 1857, Pasteur convinced the scientific community that all fermentations are the results of microbial activity. He showed that fermentation is always accompanied by the development of micro-organisms. There are many kinds of fermentation and each kind is a characteristic of particular microbial group.
Types of Fermentation
Fermentations are classified in terms of the products formed. The initial steps of carbohydrate fermentation are identical to those of respiration. The process begins with glycolysis, in which the glucose molecule is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid. Different micro-organisms proceed the further reactions in different ways. It results in the formation of various products from pyruvic acid.
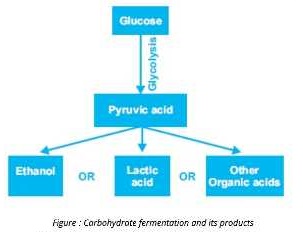
The two basic types of carbohydrate fermentation are:
1. Alcoholic Fermentation (by yeast)
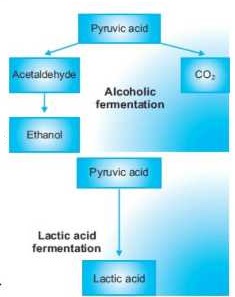
This fermentation is carried out by many types of yeast such as saccharomyces cerevisiae. This process is quite important and is used to produce bread, beer, wine and distilled spirits. In this process, carbon dioxide is removed from pyruvic acid. The product i.e. acetaldehyde is then reduced to ethanol. The carbon dioxide produced during this fermentation causes the rise of the bread.
2. Lactic acid Fermentation (by bacteria)
In this process, pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid. It is carried out by many bacteria e.g. Streptococcus and many Lactobacillus species. It is quite important in dairy industry where it is used for souring milk and also for production of various types of cheese.
![]()