Q.3 Explain Components of Ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem is comprised of two basic parts
1) Biotic Components
Definition
The living parts (organisms) of the ecosystem is called biotic components, Examples
• Producers (Plants, Algae and Cyanobacteria)
• Consumers (Animals, Protozoa)
• Decomposers (Bacteria and Fungi)
2) Abiotic Components
The non-living factors present in ecosystem are called abiotic components.
Examples
i) Air ii) Water iii). Soil iv) Light v)
Temperature Biotic Components
1) Producers
Definition
These are the autotrophs in an ecosystem. These organisms are able to synthesize complex organic compounds (food) from inorganic raw materials. Producers form the basis of any ecosystem.
Examples
(i) In terrestrial ecosystems, plants are the main producers.
(ii) In aquatic ecosystems, the main producers are the algae (phytoplankton) and Shallow water rooted plants.
2) Consumers
Definition
These are the heterotrophs in an ecosystem. These organisms are unable to synthesize their food and so depend upon producers for food. The animals are the major consumers of all the ecosystems.
Examples
Animals, Fungi, Protozoans and many of the Bacteria.
Types of Consumers
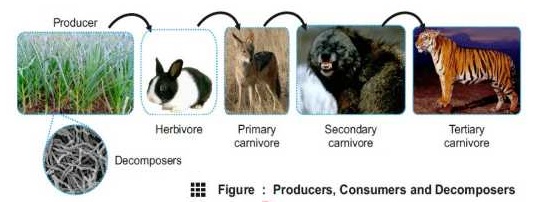
i. Herbivores
These animals feed directly on plants or products of plants. They are also called primary
consumers.
Examples
Cattle, deer, rabbit, grasshopper etc.
ii. Carnivores.
Those animals that feed upon other animals are called carnivores. The carnivores are of following types.
Types of carnivores
a) Primary carnivores
Those carnivores that feed upon herbivores are called primary carnivores. They are secondary consumers.
Examples
Fox, frog, predatory birds, many fishes and snakes.
b) Secondary carnivores
Those carnivores that feed upon primary carnivores are called secondary carnivores. They are tertiary consumers.
Examples
Wolf and owl etc.
c) Tertiary carnivores
Those carnivores that feed upon secondary carnivores are called tertiary carnivores. They are not eaten by any other animals. So they are also called top carnivores.
Examples
Lion, Tiger etc.
Omnivores
Those consumers that eat animal flesh as well as plants and plant products are called omnivores. :
Examples
Human and Crow etc.
3) Decomposers or Reducers
Those organisms that break down the complex organic compounds of dead matter (of plants and animals) into simple compounds. They secrete digestive enzymes into dead and decaying organic matter to digest the organic material. Products of digestion are absorbed for their own use and remaining substances are added to the environment for reuse. The minerals, which are released by decomposers, are used as nutrients by the producers.
Examples
Bacteria and fungi.
![]()