Q.12 What is endocrine system. Describe important endocrine glands.
Answer:
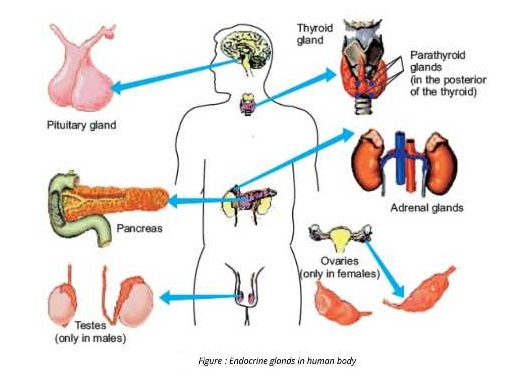
Endocrine Glands
Introduction
Endocrine system regulates the activities such as growth, reproduction, maintenance of glucose concentration in blood, reabsorption of water in kidneys etc.
Hormones
Endocrine system uses chemicals to communicate with its effectors. These chemicals are known as hormones. A hormone is a specific messenger molecule synthesized and secreted by endocrine gland.
Types of Gland
They are of two types:
(a) Endocrine Gland
These glands are ductless and release their secretions (hormones) directly into the blood stream. Blood carries the hormone to the target organs or tissues upon which they act.
(b) Exocrine glands
Many glands in our body are exocrine. Such glands have ducts for releasing their secretions e.g. digestive glands, skin glands etc. Important Endocrine glands 1. Pituitary Gland Structure
It is a pea-shaped gland. Location
It is attached to the hypothalamus of brain.
Hormones
Many hormones of pituitary gland influence the secretions of other endocrine glands. However some hormones of this gland act directly on various tissues of body. Lobes of pituitary gland
There are two lobes of pituitary gland. (a) Anterior lobe Hormones
It produces many hormones.
(i) SOMATOTROPHIN
One of its important hormone is somatotrophin (growth hormone).
Function
It promotes the growth of body.
Deficiency – Dwarfism
If the production of this hormone is diminished during growing age, the rate of growth decreases. This condition is called dwarfism.
Over Production-Gigantism
If this hormone is excessively produced after growing age, it leads to gigantism (very tall and overweight).
Acromegaly
If this hormone is excessively produced after growing age, internal organs and body extremities alone grow large. This condition is known as acromegaly. Such persons will have large hand, feet and jawbones.
(ii) Thyroid stimulating hormone
Another important hormone secreted by the anterior lobe of pituitary gland is Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
Function
It stimulates thyroid gland to secrete its hormones. The remaining hormones of anterior, lobe influence reproductive organs and also control adrenal glands.
(b) Posterior Lobe
(a) Hormones
The posterior lobe of pituitary gland stores and secretes two hormones i.e. oxytocin and vasopressin (Antidiuretic Hormone ADH).
(b) Production of Hormones
These hormones are produced by hypothalamus.
Functions
(i) Vasopressin
(a) Retaining water and less amount of urine
It increases the rate of reabsorption of water from nephrons. When we have low amount of water in body fluids, pituitary gland secretes vasopressin and so more reabsorption of water occurs from nephrons into blood. In this way, body retains water and less amount of urine is produced.
(b) Less water reabsorption and more amount of urine .
On the other hand, when body fluids have more than normal water, there is a decline in
the secretion of this hormone. If pituitary gland does not secrete this hormone in the required amount, less water is reabsorbed from nephrons and there is excessive loss of water through urine. This condition is known as diabetes insipidus.
(ii) Oxytocin
This hormone stimulates the contraction of uterus walls in mothers for child birth.
It is necessary for the ejection of milk from breast
2. Thyroid Gland
This is the largest endocrine gland in the human body. It produces two hormones.
Location
It is present in neck region below the larynx.
i. Thyroxin Hormone
It produces a hormone thyroxin. Iodine is required for the production of this hormone.
Deficiency .
If a person lacks iodine in diet, thyroid gland cannot make its hormone. In this condition, thyroid gland enlarges. This disorder is called goitre.
Hypothyroidism is caused by the under production of thyroxin.
Effects
Low energy production in body, slowing down of heartbeat.
Over-production
Hyperthyroidism is caused by over-production of thyroxin.
Effects / Symptoms
(i) Increase in energy production
(ii) Increase heart beat
(iii) Frequent sweating
(iv) Shivering of hands
Function of Thyroxin
Thyroxin increases the breakdown of food (oxidation) and releases energy in body. It is also responsible for the growth of body.
ii. Calcitonin Hormone
The thyroid gland produces another hormone called calcitonin.
Effects
It decreases the level of calcium ions in blood and promotes the absorption of calcium from blood into bones.
3. Parathyroid gland
Location
These are four glands situated on the posterior side of thyroid gland.
Hormone
This gland produces a hormone known as parathormone.
Function
It increases the level of calcium ions in blood.
Over – production
When there is an increased production of parathormone, more than normal calcium salts are absorbed from the bones and added to blood. Consequently, the bones become brittle.
Deficiency
If there is deficiency in the production of parathormone, blood.calcium level falls. It. leads to tetany which affects the function of muscles.
4. ADRENAL GLANDS
Location
Two adrenal glands are situated above the kidneys.
Structure
Each adrenal gland consists of two parts;
i. Cortex
The outer part is cortex.
ii. Medulla
The inner part is medulla.
Hormone of adrenal medulla
Adrenal medulla secretes a hormone called epinephrine or adrenaline in response to stress.
Emergency Hormone
It prepares our body to overcome emergency situation. Therefore adrenaline is also termed as an emergency hormone. Hormone of Adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex secretes many hormones called corticosteroids which maintain the balance of salts and water in blood.
5. Pancreas
This organ has two functions:
Pancreas as Exocrine Gland
The major part of pancreas is a ducted (exocrine) gland. This portion secretes digestive enzymes through a duct into the small intestine.
Pancreas as Endocrine Gland
Some portions of pancreas serve as ductless (endocrine) gland. This portion contains groups of endocrine cells referred to as Islets of Langerhans.
Hormones of Islets of Langerhans
The islets secrete two hormones i.e. insulin and glucagon.
(i) GLUCAGON
“It influences the liver to release glucose in blood and blood glucose concentration rises.
(ii) INSULIN
It influences the liver to take excess glucose from blood and so the blood glucose concentration falls.
Deficiency of insulin
If a person’s pancreas does not make normal quantity of insulin, the blood glucose concentration rises and the person suffers from diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms of diabetes
Persons with diabetes have:
i. Loss of weight
ii. Weakening of muscles
iii. Tiredness
Treatment of diabetes
Diabetes can be controlled by insulin administration. Formerly insulin extracted from animals was used for this purpose. But now. human insulin produced from bacteria through genetic engineering is available.
6. GONADS Definition
Testes and ovaries are the male and female reproductive organs respectively. They are collectively called gonads.
Testes
Testes secrete hormones e.g. testosterone, which is responsible for the development of male secondary sex characters such as growth of hair on face and coarseness of voice etc.
Ovaries
Ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone which are responsible for the development of female secondary characters such as the development of breast.
Thyroid gland
![]()